Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Architecture
In contrast to the Client-Server Architecture, Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Architecture facilitates direct communication and resource sharing between individual devices without relying on a centralized server. Imagine a network where various devices, such as computers or smartphones, are interconnected, allowing them to exchange data and services seamlessly.
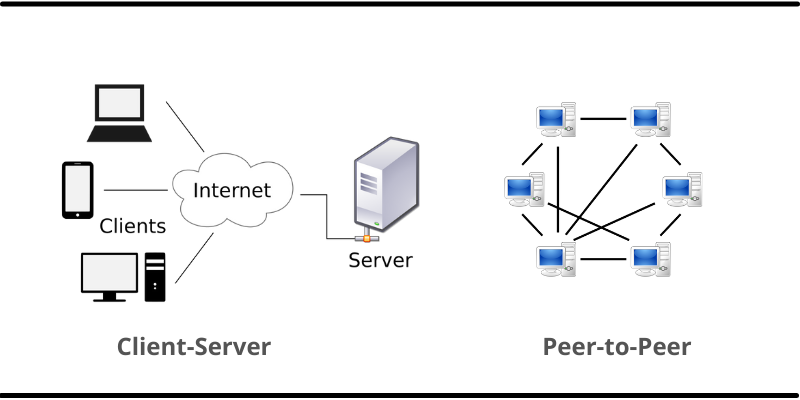
Key Characteristics
Decentralization:
Unlike the Client-Server model, where a central server manages communication, P2P networks distribute the workload across multiple devices. Each device functions both as a client and a server, capable of initiating requests and responding to others.
Scalability:
P2P networks offer inherent scalability, as new devices can join the network easily, expanding its capacity without the need for additional infrastructure. This flexibility enables rapid growth and adaptation to changing demands.
Examples and Use Cases
A prominent example of P2P architecture is BitTorrent, a file-sharing protocol widely used for distributing large files across the internet. In BitTorrent, users known as "peers" connect to each other directly to share portions of a file, such as a movie or software application. This decentralized approach allows for faster downloads and reduces reliance on centralized servers.
Hybrid Models
While P2P architecture is typically associated with decentralized networks, hybrid models also exist. These models combine elements of peer-to-peer communication with centralized components, such as databases or authentication servers. This hybrid approach offers a balance between the scalability of P2P networks and the reliability of centralized systems.
Peer-to-Peer architecture offers an alternative paradigm for network communication, emphasizing decentralization, scalability, and direct device-to-device interaction. Whether facilitating file sharing, collaborative computing, or distributed applications, P2P networks provide a versatile framework for diverse use cases in the digital realm.
