topologies
A network topology is the physical and logical arrangement of nodes and connections in a network. Nodes usually include devices such as switches, routers and software with switch and router features. Network topologies are often represented as a graph.
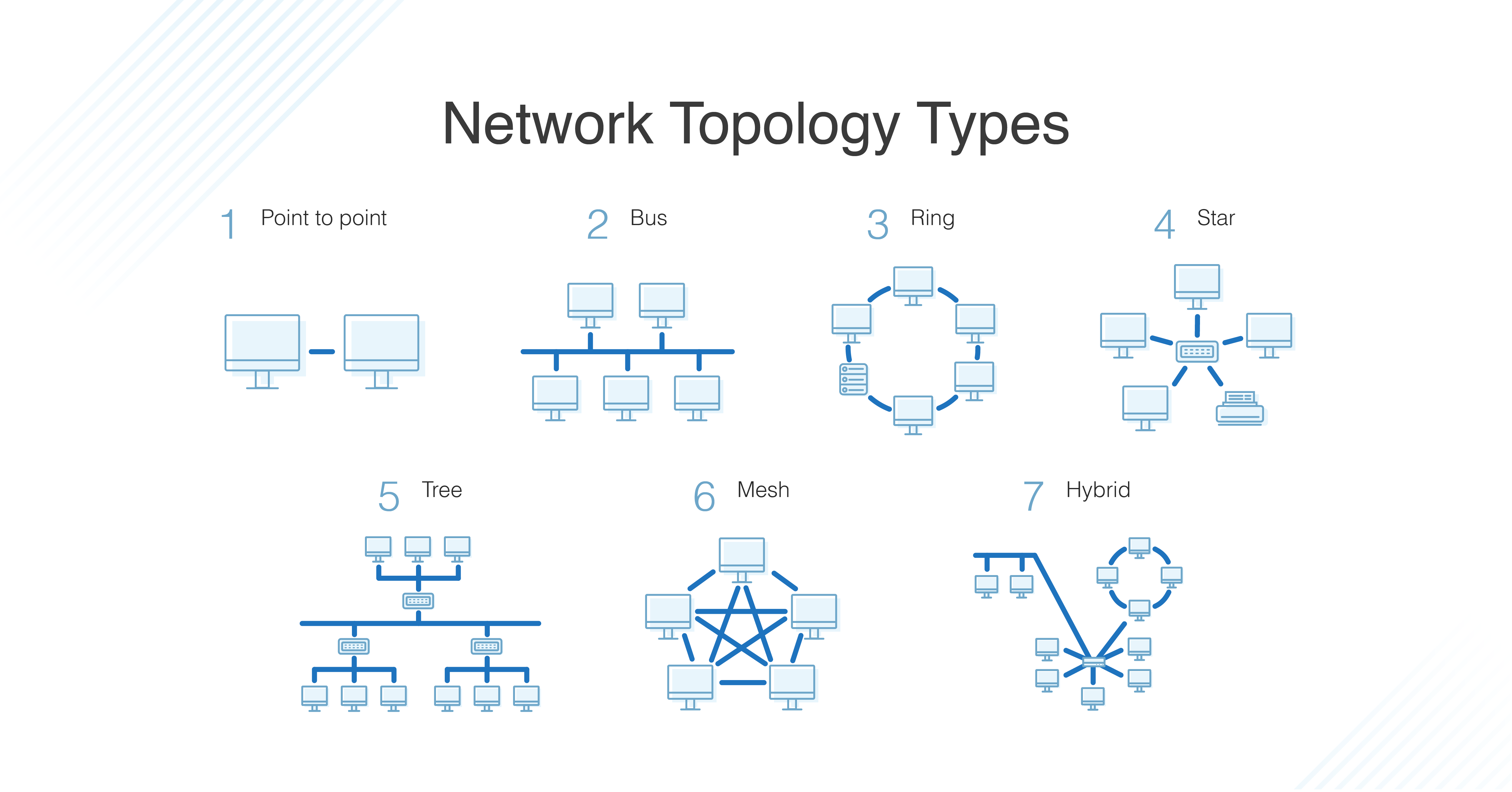
bus topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable or backbone. The main cable acts as the communication medium, with devices connected through drop lines. Data travels in one direction around the loop, passing through each device until it reaches its destination. This type of topology is easy to set up and inexpensive, but it can be susceptible to failure if the main cable breaks. Additionally, only one device can transmit data at a time, which can lead to bottlenecks.
ring topology
In a ring topology, devices are connected in a circular manner, with each device connected to exactly two other devices, forming a closed loop. Data travels in one direction around the ring, passing through each device until it reaches its destination. This type of topology can be more reliable than a bus topology because data can still flow even if one device fails. However, it is also more susceptible to cable breaks, as a single break can disrupt the entire ring. Additionally, data collisions can occur if two devices try to transmit data at the same time.
star topology
In a star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. Communication between devices occurs through the central hub, which manages data traffic. This type of topology is easy to set up and manage, and it is less susceptible to failure than bus or ring topologies. However, the central hub is a single point of failure, so if it fails, the entire network will go down.
tree topology
A tree topology combines elements of bus and star topologies. It consists of multiple star networks connected in a bus-like structure. Each star network has its own central hub, and these hubs are connected to a main bus or backbone. This type of topology offers better fault tolerance than bus or star topologies because data can still flow even if one branch of the tree fails. However, it can be more complex to set up and manage than other topologies.
mesh topology
In a mesh topology, every device is connected to every other device in the network. This type of topology offers redundancy and fault tolerance, as multiple paths exist for data transmission. However, mesh topologies can be expensive to implement and maintain due to the extensive cabling required, and scalability can be challenging as adding new devices increases complexity.
Overall, each topology has its advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on factors such as network size, reliability requirements, and budget constraints. Understanding these topologies is essential for designing and managing network infrastructures effectively.
